IoT-Lab2 Experiment Report
Lab2 Connect CounterFit Device to the Cloud
What are sensors?
Sensors are hardware devices what sense the physical world - It means that they measure one or more properties around them and send the information to an IoT device. Sensors cover a huge range of devices because there are so many things that can be measured, from natural properties such as air temperature to physical interactions such as movement.(such as “light” in the homework(Lab1) I did before)
some common sensors include:
Temperature sensors - these sense the air temperature or the temperature of what they are immersed in. For hobbyists and developers, these are often combined with air pressure and humidity in a single sensor.
Buttons - these sense when they have been pressed.
Light sensors - these detect light levels and can be for specific colors, UV * light, IR light, or general visible light.
Cameras - these sense a visual representation of the world by taking a photograph or streaming video.
Accelerometers - these sense movement in multiple directions.
Microphones - these sense sound, either general sound levels or directional sound.
What are actuators?
Actuators are the opposite of sensors - they convert an electrical signal from your IoT device into an interaction with the physical world such as emitting light or sound, or moving a motor.(such as “LED” in the homework(Lab1) I did before)
some common actuators include:
LED - these emit light when turned on
Relay - these are switches that can be turned on or off by an electrical signal. They allow a small voltage from an IoT device to turn on larger voltages.
Message Queueing Telemetry Transport (MQTT)
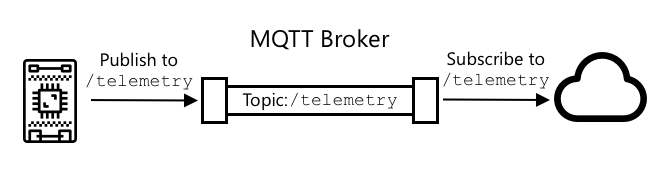
MQTT is a lightweight, open standard messaging protocol that can send messages between devices. It was designed in 1999 to monitor oil pipelines, before being released as an open standard 15 years later by IBM.
MQTT has a single broker and multiple clients. All clients connect to the broker, and the broker routes messages to the relevant clients. Messages are routed using named topics, rather than being sent directly to an individual client. A client can publish to a topic, and any clients that subscribe to that topic will receive the message.
Easy to say:
MQTT is a messaging protocol.It allows a device can send messages to another device.(like a cloud maybe?)
Task
To connect a light sensor and a LED actuator through a virtual device.This system collects the light level of the environment and send the result to the server.The server determines that if the light level is less than 300,it will send a control instruction to the device through the MQTT broker to make the LED light up.
Preparing for the task
Ensure the terminal is running the virtual environment.If your terminal is not running the virtual environment,you should configure a Python virtual environment.
- create and navigate to a new directory
1 | mkdir nightlight-server |
- create a virtual environment in the .venv folder
1 | python3 -m venv .venv |
- Activate the virtual environment
on Linux,run:
1 | source ./.venv/bin/activate |
Install the MQTT pip package:
1 | pip3 install paho-mqtt |
I installed it before:

Make your app could communicate over MQTT
To make your app to communicate over MQTT,we should add the paho,mqtt.client library.
So according the file named “app.py” in Lab1,we should add the following import to the top of the it.
1 | import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt |
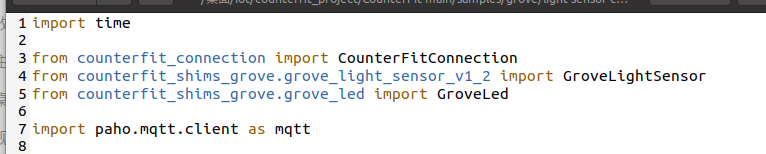
Add the following code after defining the light sensor and LED:
1 | id = '<ID>' |
Replace
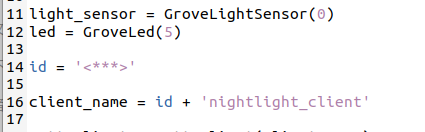
The client_name is a unique name for this MQTT client on the broker.
Create the client object and connect to the public MQTT broker
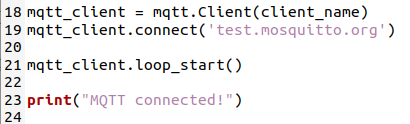
Add the following code below this new code to create an MQTT client object and connect to the MQTT broker:
1 | mqtt_client = mqtt.Client(client_name) |
This code creates the client object, connects to the public MQTT broker, and starts a processing loop that runs in a background thread listening for messages on any subscribed topics.
The task is to make the LED lights up when the light sensor level less than 300.The following is the code:

And this is the whole code:
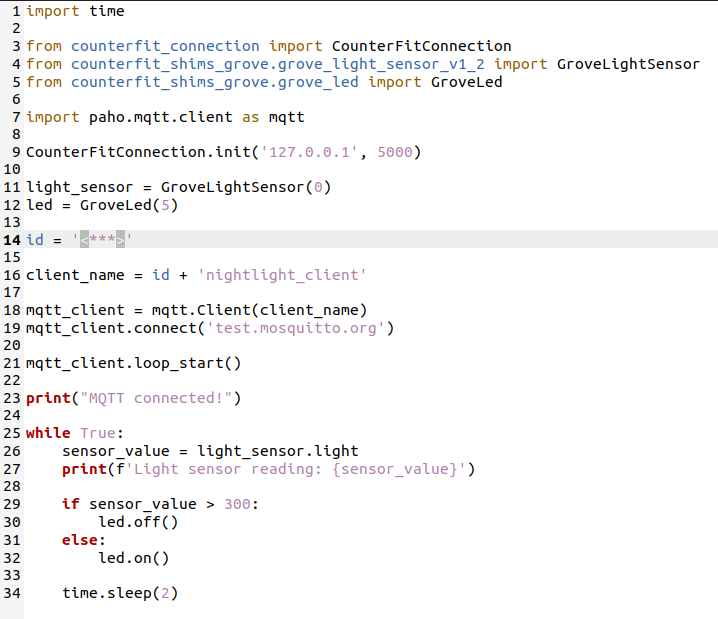
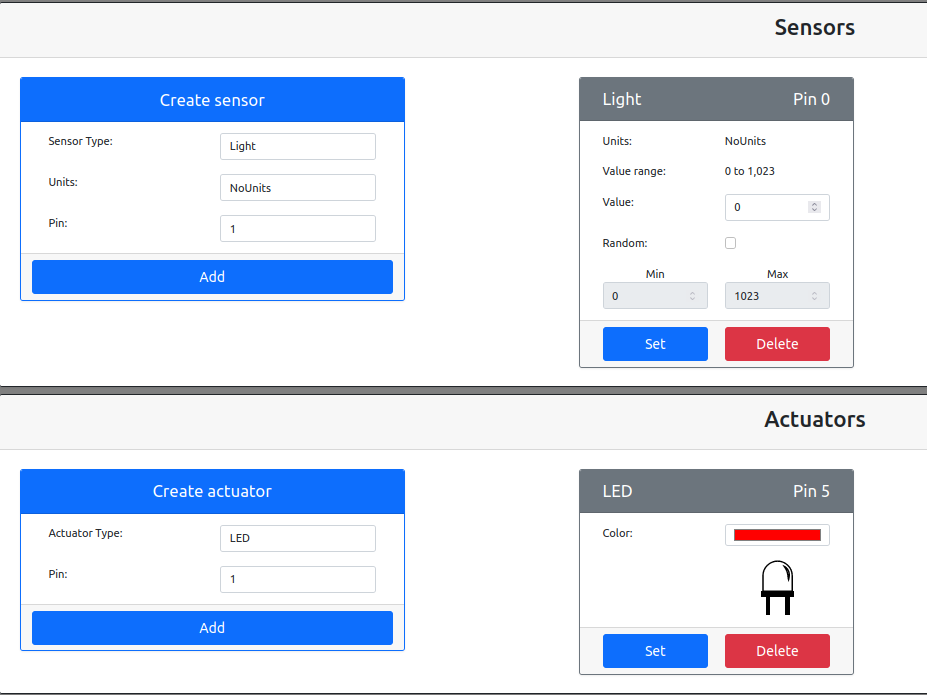
tips:according to the code,the number of light sensor should be “0” and the number of LED actuator should be “5”.
Running
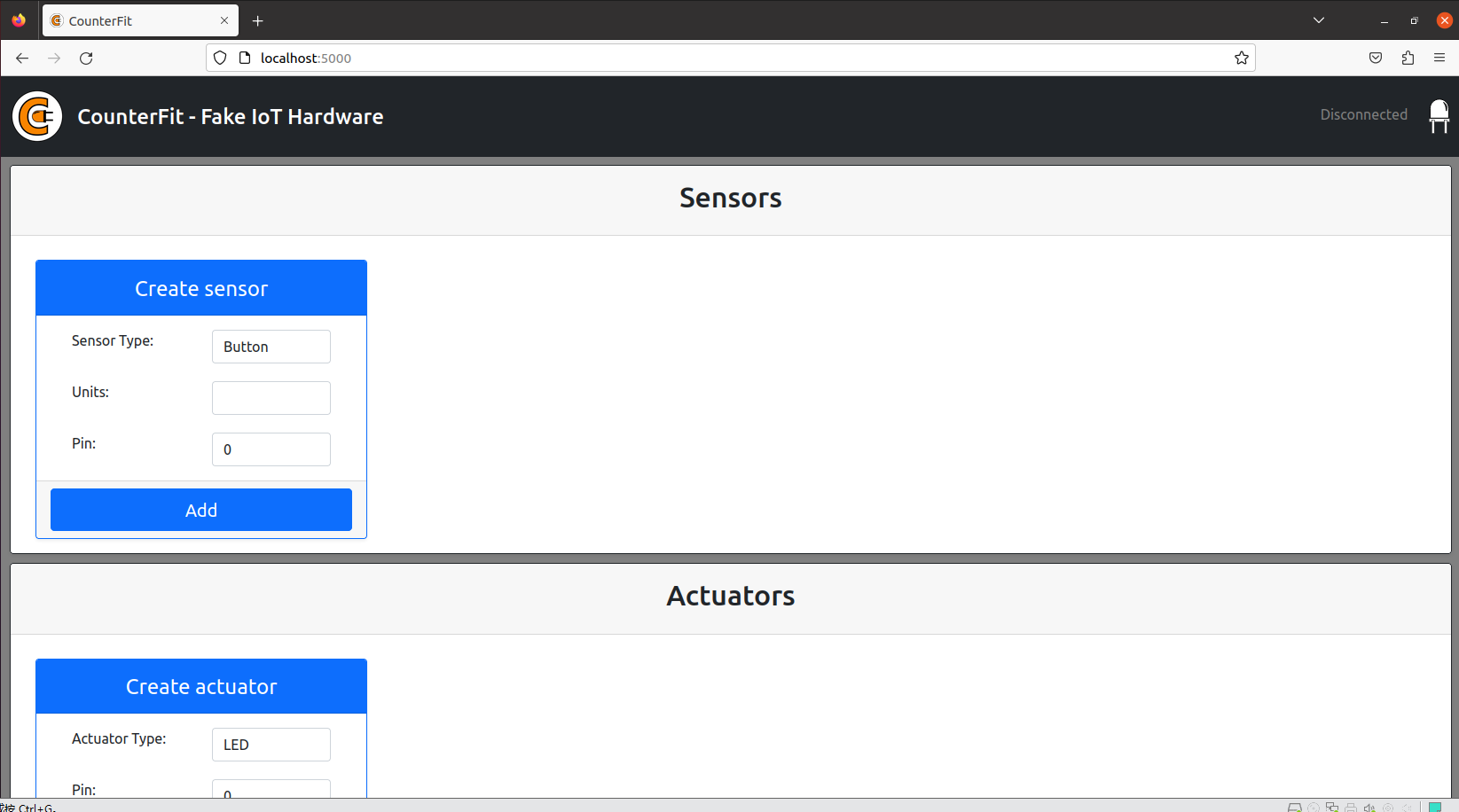
Run the app(counterfit) and open a browser to connect with it.
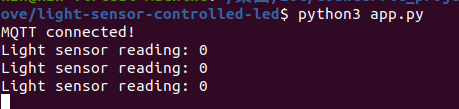
Run the “app.py” to connect the app with MQTT and also connect the app with the Internet.

We can see that “MQTT connected”
Create sensor and actuator.(Do you remember that the number of them ?)
Run the “app.py” again.
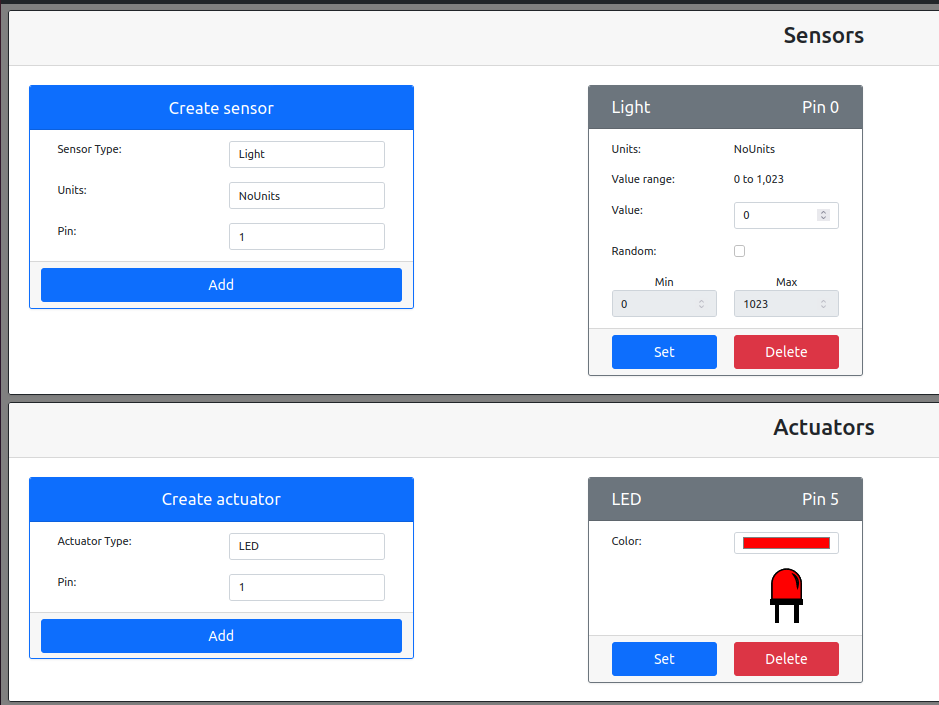
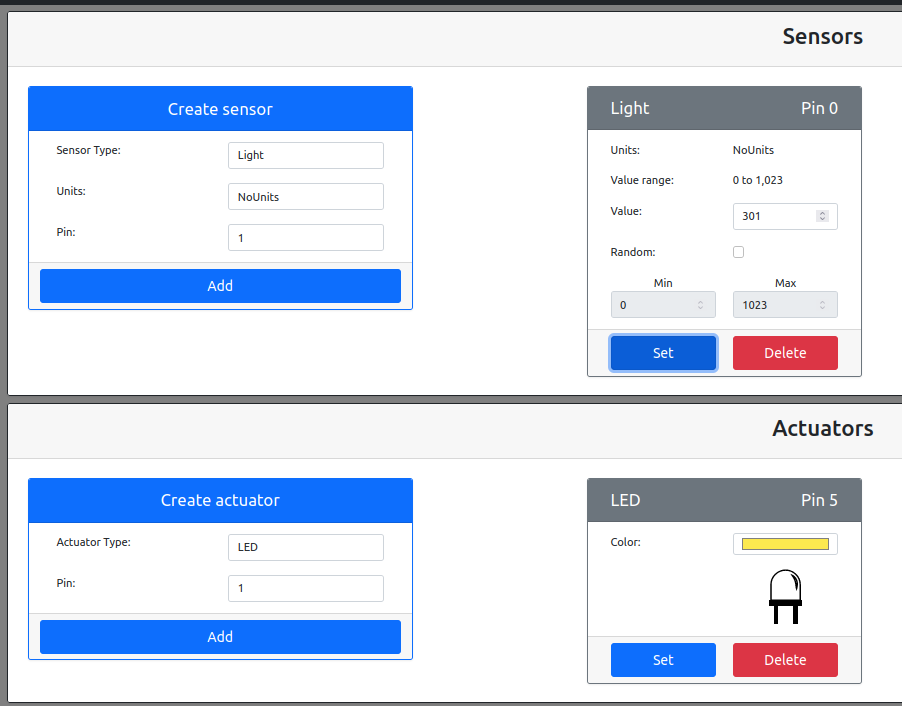
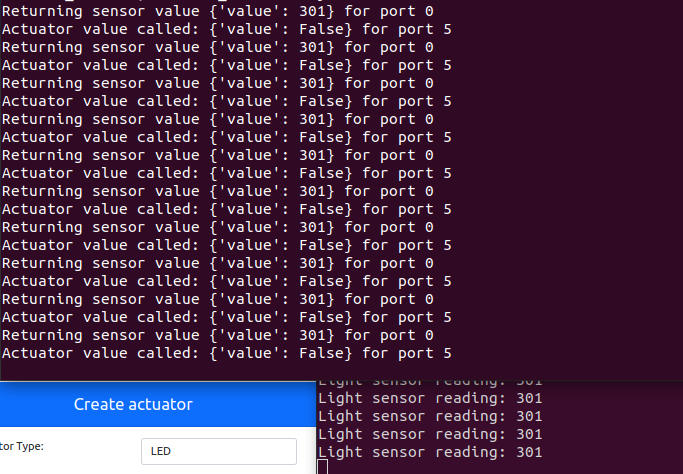
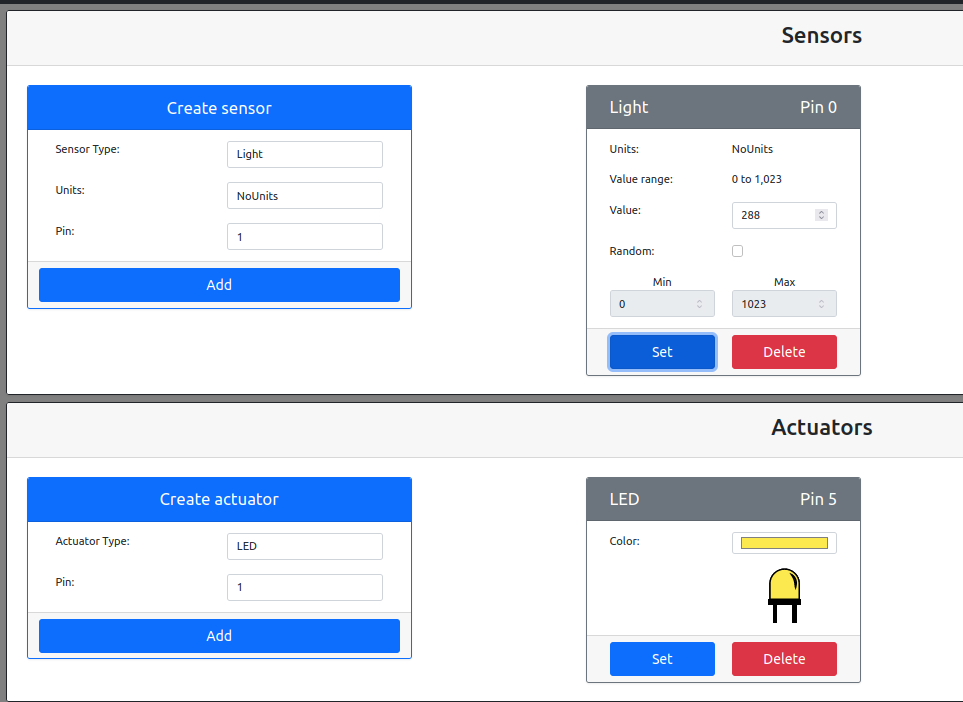
When we chage the light level to a value more than 300,LED lights off.And chage the light level to a value less than 300,LED lights on.
Now,we finish our homework.